FFT = Fast Fourier transform
Engineering Terminology for artists
Will be focussing on continuous digital data: 1D sensors and 2D signals (images)
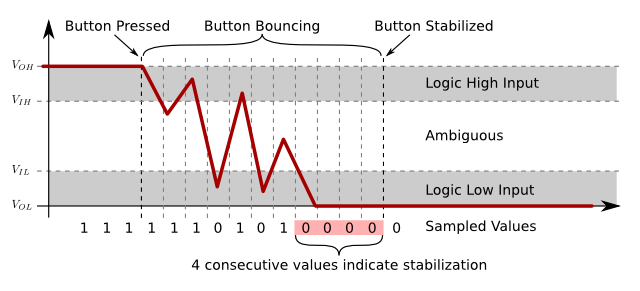
Even buttons have noise. Media artists must deal with noise:
Signals:
amplitude, frequency, period
Timbre: the shape of the wave (ex: square, ragged, curved)
Phase: phase must have two waves in relation to each other. They can cancel subtract or add to each other.
Pulse Width Modulations: duty cycle is the amount of time something is on
Spatial Frequency: visual signals have it all too ( amplitude, frequency, period and orientation)
different spatial frequencies convey different things about about an images:
high = detail, low = blur
Digital Signals:2 numbers characterize the sampling resolution:
Bit Depth
Sampling Rate
Nyquist Rate & Aliasing: nyquist rate is 1/2 the sampling rate. Any frequency higher than two times the sampling rate will be aliased ( distorted and represented as a lower frequency)
line fitting: least squares line fitting. opencv
Forier: ways of representing a complex sound as a combination of different waves. This allows you to re-create a sound. see visually in stereography
can also see the the fft of an image. (has orientation unlike stereography) can reconstruct an image from its fft.
Noise:
Gaussian noise is most common when observing natural processes
shot noise: bad individual samples (sporadic pops)
Drift noise: linked to time. where sensor becomes degraded
Filtering:
local averaging: local filters average of surrounding local values (use a copy buffer)
median average: gets rid of spot noise really quickly.
Winsorized Averaging: is a combination of median and averaging. It cuts off extreme values and then it averages.
convolution kernel filtering (2D): replacing my value with that of my neighbors. Can give different weights to different pixels/
kernel: 3×3 equal weights. can use it to detect edges etc. ( use imagej to write own filters)
gaussian: 7×7 pays less attention to corners.
Histograms: thresholding – determining foreground and background.
finding the best thresholding: use the random triangle method that usually works. eyeo thresholding is the intersection between different curves. iso thresholding.